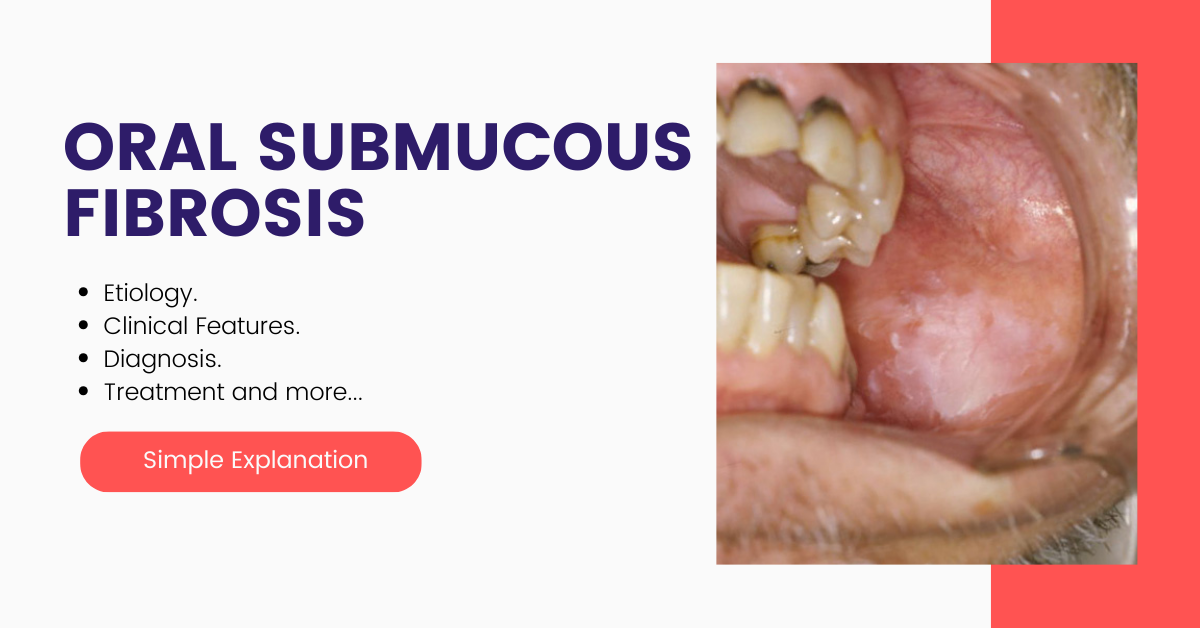
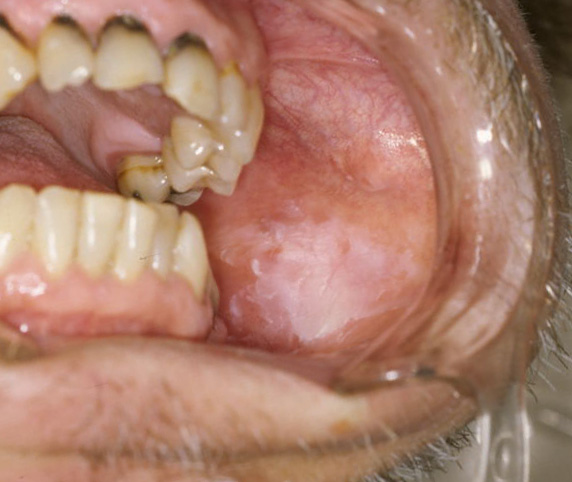
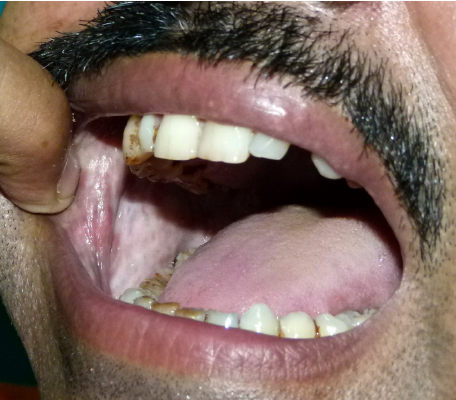
OSMF is known as oral sub-mucous fibrosis. It is a disease seen in the oral cavity and in severe cases spreads outward and sometimes to the pharynx. It is a premalignant [premalignant means tissues which are not yet malignant but they are yet to become malignant in the future] disease resulting from the to addiction tobacco. It causes stiffness of the oral mucous lining, trismus, and inability to eat food.
The main cause of oral sub-mucous fibrosis is to use of tobacco and pan masala.
Contents
ETIOLOGY
The main cause of oral sub-mucous fibrosis is tobacco chewing and it is a known irritant. The use of chilies may cause oral sub-mucous fibrosis and the patient complains of having a burning sensation while having spicy food. Most of the people in India use beetle nuts for chewing. The lime which is used with the beetle for chewing causes local irritation and damage to the mucosa and results in ulcer formation. It also acts as a local irritant
The other cause of it is nutritional deficiency. Lack of nutritional deficiency especially vitamin B12 has been suspected in this case.
Studies have shown that defective in the metabolism of iron also cause oral sub mucous fibrosis.
HOW IT LOOKS CLINICALLY?
Oral sub-mucous fibrosis is characterized by inflammation and fibrosis [ fibrosis means the formation of the fibrous band] of the sub-mucosal tissue which results in rigidity [stiffness] and restricted opening of the mouth called a trismus.
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF OSMF?
The symptoms of Oral Sub mucous Fibrosis are listed below:
In early stages:
1. In the initial stage patient complained of a burning sensation in the mouth while eating especially spicy food.
2. Blister formation and ulceration are seen in the mouth.
3. Either Hypersalivation of Xerostomia or dryness of mouth are seen.
4. Pigmentations are seen in the cheek mucosa, tongue, gums, or gingival.
In advanced stages:
- In advanced stages blanching [blanching means the oral mucosa looks marble-like appearance] can be seen in the buccal mucosa [lining inside the cheek]. The blanched mucosa becomes slightly opaque and white in color. The whitening looks like spots on the mucosa and acquires a marble-like appearance
- Fibrous bands are seen which are vertical in nature. When we palpate these bands with a finger roughness can be felt and they are easy to palpate.
- In the initial stage, the tongue becomes depapilatation usually in the lateral margins. The tongue becomes smooth when we touch and the mobility of the tongue when we move becomes restricted especially when we protrude.
- When the floor of the mouth is affected it becomes inelastic in nature.
- The gingival or the gums look fibrotic, blanched, and inelastic.
- There will be difficulty in whistling and blowing due to the deposition of the fibrous band.
- Inability to swallow the food.
- Referred pain in the ear and deafness
- Most of the patient comes to visit the doctor with a complaint of a burning sensation in the mouth and restricted mouth opening. Normally four fingers should enter the mouth but in case of oral sub mucous fibrosis, it becomes three or two fingers.
- Also, we can measure the mouth opening with a scale. The measurement will be less than 5cm.
SITE OF DISTRIBUTION
The most common location of oral sub-mucous fibrosis is the buccal mucosa or the cheek mucosa and the retromolar area. It is also seen in the soft palate, palatal fauces, tongue, and labial mucosa. In Some cases, they are seen on the floor of the mouth and the gingival too.
GRADING OF OSMF
There are certain grading that help us to identify at which stage the oral sub-mucous fibrosis and this helps for better treatment aspects.
There are four grades:
Grade 1
Grade 1 is called the incipient stage. It is the very early stage. In this stage, the mouth opening is normal which is 44mm and when we move the tongue protrusion is also normal, or in other words, it said that no abnormality was detected.
Grade 2
Grade 2 is known as mild. There is a slight restriction of mouth opening that is it ranges between 26-35 mm. When we move the tongue the movement is normal or in other words, no abnormality is detected.
Grade 3
Grade 3 is known as the moderate stage in which there is considerable restriction of mouth opening which ranges between 15-25mm. when we protrude the tongue it is not that much affected but the patient feels difficulty in eating and speaking. When we observe the mouth’s poor oral hygiene.
Grade 4
Grade 4 is known as the advanced stage. In this stage when we protrude the tongue there is restricted tongue movement. Difficulty in eating food and speech is also very much impaired due to restricted mouth opening. The hygiene of the mouth is very poor.
Grade 5
Grade 5 is known as an advanced premalignant and malignant stage where all the signs of oral sub-mucous fibrosis can be seen and it is associated with leukoplakia and lichen planus.
IS OSMF A DANGEROUS DISEASE??
Yes, oral sub-mucous fibrosis is a dangerous disease with a high morbidity rate. So early detection helps for better recovery.
Due to the burning sensation and restricted mouth opening the intake of food will be less and the patient will feel weaker.
So consult a physician as soon as you observe the symptoms.
WILL OSMF CAUSE CANCER?
Yes, oral sub-mucous fibrosis will cause cancer if you are not treated at the right time. As I mentioned in the beginning it is a premalignant disease, which means it can become a cancerous one.
WHAT CAN BE DONE?
Quit the use of arecanut chewing, tobacco, or smoking cigarettes. The use of tobacco can worsen the situation. The use of tobacco should be stopped permanently.
DIAGNOSIS
A clinically reduced mouth opening with the palpable fibrous band is enough to make a diagnosis.
Laboratory diagnosis includes oral epithelium is taken and observed under the microscope. As I mentioned earlier it is inflammatory in nature. When we observe under the microscope inflammatory cells, which are mononuclear eosinophils and plasma are seen.
HOW OSMF IS TREATED?
Oral sub-mucous fibrosis is well known for its chronic nature and many consequences. There are various treatment modalities available to treat this condition such as medical approach, surgical approach, and physiotherapy. And now the latest is the use of LASER.
How do the proper treatments begin?? The proper treatment begins by educating the patient by talking about the ill effects of arecanut, the side effects of tobacco, pan, etc. The patient should be educated about the irreversible nature of the disease and getting into a cancerous condition.
First, when you come to the clinic the physician judge the treatment by checking your mouth opening. As I mentioned before there are different grades of oral sub mucous fibrosis. First, we will check which grade it is. If it is in the earlier grade then the treatment would be easier and the chance of getting it cured would be high in other words, it is reversible.
Restriction of the habit and behavioral therapy
First, the patient should stop the habit, especially the use of tobacco, pan, etc.
The doctor will explain the disease and in which stage you are in. Improvement in the clinical features can be seen like a gradual increase in the interincisal opening in recall check when the patient quit the habit.
Medical therapy
Supportive treatment
The medical therapy includes vitamin vitamin-rich diet and Iodine B complex preparation.
The vitamin-rich diet along with iron preparation is helpful to some extent but it has little therapeutic value for reliving trismus.
Iodine B complex preparation: The iodine B complex preparation is a mixture of iodine and vitamin B complex. This combination helps stimulate of metabolic process and enzymatic process within the body.
Steroids
The most commonly used steroids are hydrocortisone injections. The combination of hydrocortisone with procaine hydrochloride injection locally in the area of fibrosis helps for early cases and shows good improvement when they are used in early cases. This is the local route.
The systemic route includes therapy with hydrocortisone 25mg tablet in doses of 100mg per day. This medication helps relieve the burning sensation without any sought-after side effects to the patient.
Vitamin E
The use of vitamin E along with steroids helps for better recovery.
Surgical treatment
When do we go for surgical treatment??
The surgical treatment is done when there is a marked limitation in the opening of the mouth and when the neoplastic changes are seen in the biopsy. Also with trismus and dysphasia.
Flap use as a graft
The fibrous band that is deposited in the mouth is excised under local anesthesia and the tongue flap is used because the tongue is highly vascular and also resists form further formation of fibrosis.
This helps us to eliminate the trismus, and to prevent further fibrosis. This is done in patients with mouth opening less than 1.5cm. Also in case when the conservative treatment as mentioned above fails.
Oral stent
Use of oral stent as an adjunct to treatment of oral sub mucous fibrosis. What is a stent?? A stent is an appliance made up of acrylic. They are done before surgery to increase the mouth opening and also help the tissue to heal.
Laser
The laser is the newly introduced one. The laser used is a CO2 laser.
The laser technique helps alleviate the functional restriction when compared with the surgical method.
How it is done?? Under general anesthesia, a CO2 laser is used to incise the buccal mucosa and vaporize the sub-mucosal connective tissue to the level of the buccinator’s muscle. Homeostasis is provided by the laser surface itself and the mouth opening is increased immediately.
Oral physiotherapy
Oral physiotherapy is done in the early stages. This includes mouth opening and ballooning of the mouth. When we do this this will exert pressure on the band.
Diathermy
It is a method of applying current. Microwave diathermy is used in early and some moderate cases. Low current is used which is 20 watts X 2450 cycles.
A definite treatment approach is always surgery along with active physiotherapy to increase the mouth opening and also prevent relapse.
CONCLUSION
As a part of the conclusion, I conclude that the single most important factor required to improve oral sub-mucous fibrosis is early detection of the disease and diagnosis of the cancer as it will be localized in an area and the chance of cure will be high. Early diagnosis of the disease helps in a life-saving role in management.
Also if the treatment is detected in the early stage stoppage of the habit is sufficient but most of the patient comes to us when it reaches moderate to severe cases which result in irreversible changes and need to go for surgical approaches.
As it is a cancerous condition commonly seen in India because arecanut chewing is common. It is a very important need to give public health speaking in oral submucous fibrosis.
Got any questions?
Then you can comment your questions below and I will try my best to revert back as soon as possible.