Welcome to another dental note in one of the best dental blog’s – DentalFry.
I am Dr.Anooja V Chandran and I am the founder of this blog and today I will be sharing an article about Irrigants in Endodontics. This article is originally for dental students, which might help them in academics.
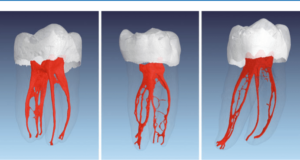
Proper shaping and cleaning of the root canal help in the removal of the debris and microbial content in the root canal. But do you think all the debris will get removed with this? No, there are certain areas in which the bacteria persist and survive. If there is any remnant pulp or microbes then it will create microbial colonies.
So the root canal treatment should be done in such a way that all the debris even the minute should be removed from the canal.
Contents
- 1 List of microbes present in the root canal
- 2 Ideal requirement for an irrigant
- 3 A list of irrigants commonly Used
- 4 Photoactivated Disinfection
- 5 Herbal irrigants
- 6 Irrigation guidelines
- 7 Factors Affecting the Efficiecy of Irrigant
- 8 Method of irrigation
- 9 Various delivery systems for irrigation
- 10 Ideal properties of irrigating needles
- 11 Micro brushes and ultrasonics
- 12 EndoVac
- 13 Conclusion
List of microbes present in the root canal
-
Prevotella intermedia.
-
Prevotella nigrescens.
-
Prevotella tannerae.
-
Prevotella multissacharivorax.
-
Prevotella baroniae.
-
Prevotella denticola.
-
Porphyromonas endodontalis.
-
Porphyromonas gingivalis.
-
Dialister pneumosintes.
-
Dialister invisus.
-
Treponema denticola.
-
Treponema sacranskii.
-
Treponema parvum.
-
Treponema maltophilum.
-
Treponema lecithinolyticum.
-
Pseudoramibacter alactolyticus.
-
Filifactor alocis.
-
Actinomyces spp.
-
Propionibacterium propionicum.
-
Olsenella spp.
-
Slackia exigua.
-
Mogibacterium timidum.
-
Eubacterium spp.
- Streptococcus anginosus.
- Streptococcus mitisi.
- Streptococcus sanguinis.
- Enterococcus faecalis.
Ideal requirement for an irrigant
- It should act as a broad spectrum.
- It should not create any toxicity to the canal.
- It should have both bactericidal and fungicidal property.
- It should show the property of disinfectant.
- It should act as a good lubricant.
- It should not create any smear layer.
- It should dissolve the necrotic tissue.
- It should have low surface tension so that it can flow in the canal.
- It should be cost-effective.
- It should be easy to use.
- It should not weaken the tooth structure.
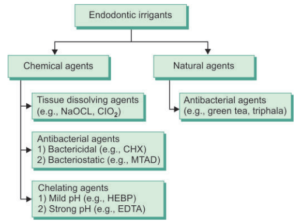
A list of irrigants commonly Used
Sodium hypochlorite
It’s a reducing agent, a clear straw-colored liquid. It contains 5% of chlorine. It is the most widely used irrigating solution.
Mechanism of action
- Sodium hypochlorite —> hypochlorous acid + hypochlorite ion.
Acts by first penetrating into the cell wall, combining the protoplasm of the cell and destruction of DNA.
Properties
- Concentration: 5.2% of sodium hypochlorite is effective. Hower 2.5% of the solution is most commonly used as it reduces side effects. If the canal is filled with the solution during the entire cleaning and shaping procedure the irrigant will act as a lubricant.
- Tissue solubility: sodium hypochlorite dissolves the entire pulp in 20 minutes to 2 hours. Some investigators have told sodium hypochlorite is less effective in narrow canals. The pulp dissolving ability of the irrigant is useful during the cleaning and shaping of inaccessible areas such as isthmus and c-shaped canals.
How to increase the efficacy of sodium hypochlorite?
- Increase the concentration of the irrigant employed.
- By warming the sodium hypochlorite at 60 – 70 degrees Celsius.
- To increase the duration of irrigation.
Drawbacks of NaOCl
- Cytotoxicity results when irrigation solution extrudes out of the canal. When we use low concentrations of sodium hypochlorite 0.5-1% or 2.5% sodium hypochlorite.
- It does not remove the inorganic component of the endodontic smear layer.
- It has an unpleasant taste
- The solution should be kept in a cool place, away from sunlight.
EDTA
We use 17% EDTA which is nontoxic and creates less irritation on weak solutions.
Mechanism of action
EDTA act by forming a calcium chelate solution with calcium ion of dentin. EDTA a chelating agent is used as an irrigant to remove the dentin, pulp, and bacteria. Some clinicians use EDTA as an irrigating solution and later clean it with hypochlorite.
|
The recommended regimen for irrigation is to employ 17% EDTA for 1 minute as a final rinse followed by NaOCl.
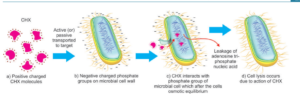
Chlorhexidine Digluconate(2%)
Chlorhexidine is used as an irrigating solution. They act as an intracanal medicament also. They possess bacteriocidal and bacteriostatic properties. Chlorhexidine is effective against E faecalis which is one of the most common pathogens identified in the root canal-filled teeth exhibiting clinical failure. The most important clinical characteristic of chlorhexidine is its substantivity which refers to sustained action within the root canal. This property helps to prevent bacterial colonization of root canal walls for prolonged periods of time.
Limitations
- chlorhexidine lacks tissue-dissolving ability
- It does not remove the smear layer and hence has to be employed in conjunction with other irrigants
Mechanism of Action
| Irrigants | Normal saline | Sodium hypochlorite | Hydrogen peroxide | EDTA | Chlorhexidine |
| concentration | 0.9% | 0.5%,1%,2.5%,5.25% | 3% | 15%-17% | 2% |
| pH | 7.3 | 10.8-12 | 6 | 7.3-8 | 5.5-7 |
| mechanism of action | physical flushing | Bactericidal | Bactericidal
|
|
|
| Advantages | No side effects, if extruded periapical | Has dissolution disinfection ad antimicrobial properties | has disinfection and antimicrobial property |
|
|
| Disadvantages | Too mild to be disinfectant | can cause tissue injury if extruded periapical |
|
||
MTAD
One of the newly introduced irrigants is MTAD- Tetracyclin, Citric acid, and Detergent. It helps to remove the smear layer.
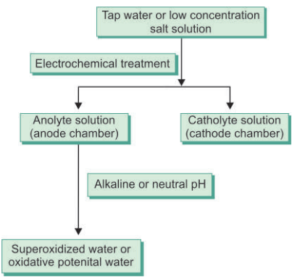
Electrochemically Activated Solution
It is produced from tap water and low-concentrated salt solution.
Advantages:
- Nontoxic biological tissues
- Effective with a wide range of microbial spectra
Combined use of NaOCl and Electrochemically activate solution shows to remove the Smealr layer
less or no reaction
Ozonated Water Irrigation
This technique is shown to be a powerful antimicrobial agent against bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and viruses.
Advantages
- Its potency
- ease of handling.
- rapid microbial effects.
- lack of mutagenicity.
Ruddle’s Solution
Its of 17% EDTA, 5% Na Cl and hypaque
Hypaque is an aqueous solution of iodide salts, namely ditrizoate and sodium iodide
The use of EDTA lowers the surface tension and allows better penetration of sodium hypochlorite
The solvent action of sodium hypochlorite clears the contents of the root canal system and thus enables hypaque components to flow into every nook and corner of the canal system such as fracture, perforation, missed canals, and defective restorations.
Uses
- Useful for visualization of root canal anatomy, missed canal, perforation.
- Helps in the diagnosis of internal resorption, its size, and site.
- Helps in the visualization of blockage, perforation, ledge, and canal transportation.
- Helps in the management of iatrogenic errors.
Photoactivated Disinfection
There are certain nontoxic photosensitizers such as methylene blue, toludine, chlorine p6 which have the property of being cytotoxic to the cells of target tissues. When the photoactivated disinfection is done, it will release oxygen and free radicles and kills the microbes.
Advantages
- Most effective antimicrobial agent.
- Effectively kills gram-positive and negative bacteria.
- Nontoxic.
- Overcomes the problems of antibiotic resistance.
- Does not cause any sensitization.
- Kills bacteria present in complex forms.
Herbal irrigants
Triphala and green tea polyphenol
- It has chelating property which helps for removing the smear layer and is rich in citric acid. Green contains anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, anticarcinogenic, and antioxidant properties. Studies show that green tea has properties that will kill the E faecalis.
Turmeric
- They have antimicrobial, anti-cariogenic, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties. they also act well against E faecalis.
Allium Sativa
- Its active components destroy the bacterial components and can be used as root canal irrigants
Propolis
- It is a substance that honey bees collect from poplars and conifers. it shows antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial activity. it is active against streptococus sorbinants and streptococus mutans.
Aloe vera
- They have both antibacterial and antifungal properties. It has been effective in E faecalis and resistant microorganisms of root canals.
Irrigation guidelines
- Rubber dam has to be used as proper isolation to prevent irrigants from coming in contact with the soft tissues.
- when you do irrigation adequate concentration, type of irrigation, and volume of irrigation, are important in cleaning and shaping.
- there are studies that show that frequent irrigation is mandatory and they are more complete in larger canals than in smaller canals.
- NaOCl is more effective when use in warm temperatures, whereas it won’t work much with other irrigants.
Factors Affecting the Efficiecy of Irrigant
- The volume of the irrigants.
- The concentration of the irrigants.
- Frequency of the irrigants.
- The temperature of the irrigants.
- Length and time of the intracanal contact.
- The gauge of the irrigating needle.
- Depth of penetration.
- Diameter of the irrigating canal.
- The use of a rubber dam is always compulsory to ensure adequate isolation of the pulp and prevent the irrigants from entering into the soft tissue.
- Adequate irrigation depends on the type, concentration, and volume of irrigants which helps for adequate irrigation.
- Frequent irrigation is very important and helps in enlarged canals where the diameter is large so proper irrigation works.
- Penetration of the irrigants is more in canals with larger diameters than the smaller diameters.
- When increasing the temperature as I mentioned above will increase the efficacy, but this won’t happen in irrigants other than NaOCl.
Method of irrigation
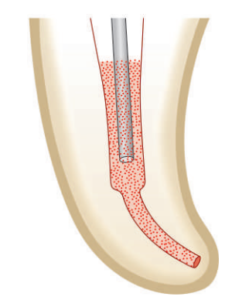
The solution should be taken adequately and slowly into the root canal. we should take loose needles so that it should not be done tightly. use blunder needles.
how to do irrigation in the case of small canals? In such cases deposit the irrigant in the pulp chamber and carry the solution by the file. never ever insert the irrigant forcefully into the canal.
how to do irrigation in case of large canals? in the case of large canals, we should feel the pressure inside the canal while irrigating.
for proper irrigation bend the needle at an angle of 30 degrees in the center of the needle. the volume of the needle is more important than the concentration.
Various delivery systems for irrigation
- Stropko irrigator.
- 27 gauge needle with a notched tip.
- Needle with bevel.
- Monojet endodontic needle.
- Pro rinse.
- Ultrasonic handpiece.
Ideal properties of irrigating needles
- Blunt.
- Allow backflow.
- Flexible.
- Longer in length.
- Easily available.
- Cost-effective.
Micro brushes and ultrasonics
Bristles are attached to braided wires and plastic cores. They have taper-like gutta-percha cones. They are used along with sodium hypochlorite and EDTA.
EndoVac
It draws the pressure apically by way of evacuation. In this case, suction is used to pull the irrigant into the canal.
Parts include:
- Master delivery tip.
- Macrocannula.
- Microcannula.
Conclusion
For a successful endodontic treatment, we should have proper irrigation for the removal of all the microbes in the root canal. For this, we should have proper instrumentation and irrigation. The most important function of irrigants is dissolving the tissue. The most commonly used irrigants are EDTA, Saline, and Hypochlorite. There are many as I mentioned in my article.
If you feel this article helped you in any way, feel free to share it with your friends and students in need.
If you are having any questions, then you can ask those in the comments below and I will try my best to reply as soon as possible. 😀